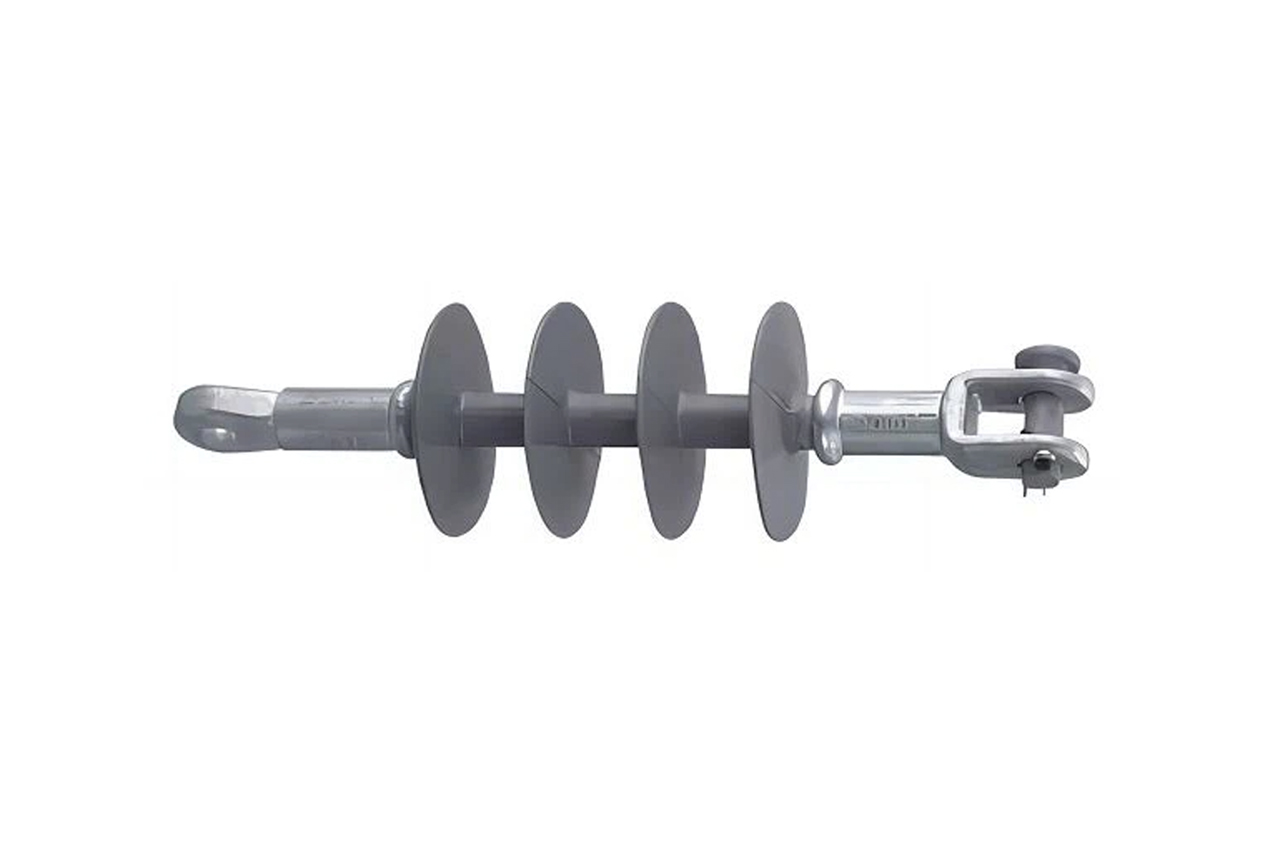
Hello! As a supplier of 20kV Composite Post Insulators, I’m often asked about their flame resistance. Let’s break down how these units perform under fire conditions.
Table of Contents
ToggleMaterial Composition and Flame Resistance
A 20kV Composite Post Insulator consists of:
Fiberglass core: High mechanical strength with a melting point exceeding 600°C, providing structural integrity during thermal exposure.
Silicone rubber housing: Inherently flame-retardant due to:
High oxygen index (typically >28%), requiring elevated oxygen concentration to sustain combustion.
Char formation: When exposed to flames, it generates a protective char layer that shields the core and halts fire spread.
Compliance with Fire Safety Standards
These insulators typically meet UL94 V-0 certification, indicating:
Self-extinguishing within 10 seconds after flame removal.
Zero flaming drips during vertical burning tests.
Additional validation often includes glow-wire ignition testing (GWIT >775°C), simulating electrical fault-induced overheating to ensure no ignition occurs.
Real-World Performance Factors
Environmental conditions significantly impact flame resistance:
Contamination accumulation (e.g., dust, pollutants): Can create conductive paths, leading to arcing and localized heating. Regular cleaning mitigates this risk.
Long-term degradation: UV exposure or extreme temperatures may reduce silicone rubber’s flame retardancy. Our formulations include UV stabilizers and age inhibitors to maintain performance over decades.
Comparison with Other Insulator Types
Porcelain insulators: Non-combustible but brittle; shatter under mechanical stress or thermal shock, posing fragmentation hazards during fires.
Composite insulators (10kV/35kV): Share similar flame-retardant mechanisms but differ in design. Higher-voltage models (e.g., 35kV) incorporate thicker silicone layers for enhanced arc resistance.
Design Enhancements for Fire Safety
UL94 V-0 compliant silicone: Prevents flame propagation and drip ignition.
Fiberglass core treatment: Fire-resistant resins boost thermal stability up to 300°C without compromising dielectric strength.
Hydrophobic recovery: Post-fire, silicone surfaces restore water repellency, minimizing contamination-related fire risks.
Applications and Selection Guidance
Ideal for:
Substations in wildfire-prone regions.
Industrial zones with high pollution levels.
When selecting insulators:
Prioritize UL94 V-0 or IEC 60695 GWIT-certified units.
Verify third-party test reports for flame resistance and tracking resistance.
References
- UL 94-1985: Test Standard for Flammability of Plastic Materials (V-0 classification criteria).
- IEC 60695-2-12: Glow-Wire Ignition Temperature (GWIT) Test Methodology.
- Silicone Rubber for High-Voltage Insulators: Aging and Fire Performance (Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2023).
- Thermal Stability of Fiberglass-Reinforced Composites in Fire Conditions (Materials Science Reports, 2024).